Why Do I Have Chronic Hives, and How Can I Manage Them?
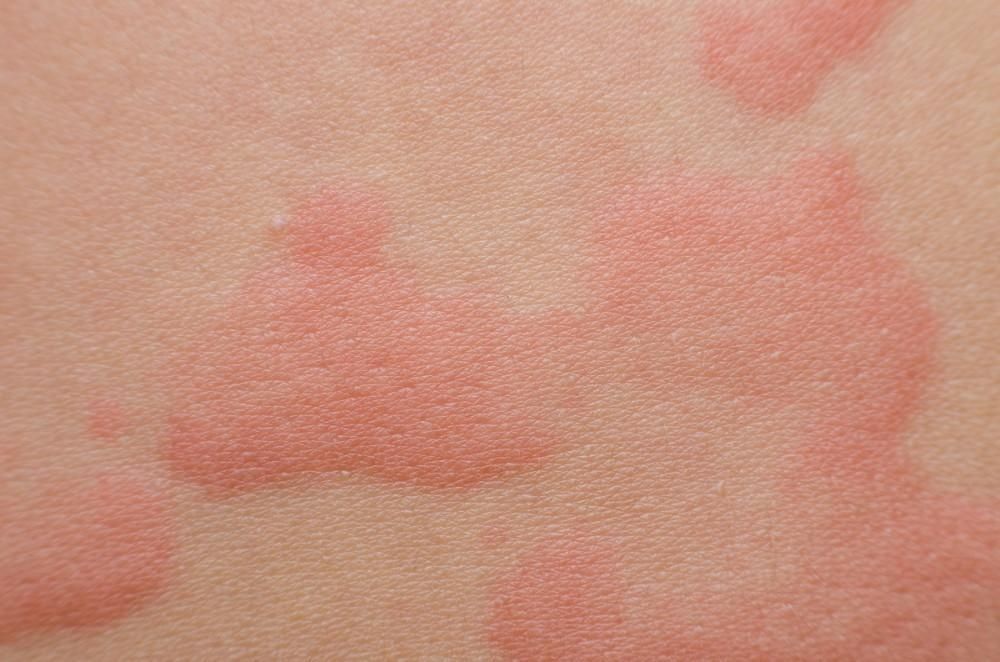
When you break out in hives, your skin is covered with raised red bumps or splotches that often look like mosquito bites. Hives can be the result of an allergic reaction to something like foods or medications. This causes your body to release histamine and other chemicals, which give you the symptoms of itching and swelling. Hives migrate across your body, fading away and then arising in another area. They can also be associated with angioedema, or swelling of the looser tissues of the face, hands, feet and groin.
Short-lived, or acute, hives can last from minutes to weeks. If you have chronic hives, however, it means they last longer than six weeks.
Having chronic hives can cause itching, which can severely affect your quality of life. The irritation makes it difficult to sleep or complete daily tasks. That’s why Mark C. Stahl, DO, and the rest of our team at Apex Allergy and Asthma located in San Antonio, Texas, want to help you get to the bottom of what’s causing your hives and offer up some ways to manage them.
Possible causes of hives
While chronic hives aren’t always caused by allergens, they might be caused by some of the following triggers:
Food in your diet
Food like shellfish, finned fish, peanuts and tree nuts might be causing you to constantly break out in hives. Sometimes food allergies are obvious. For instance, if you drink milk and break out immediately in hives, you’re probably allergic to milk. However, other times it can take much longer for hives to develop, and you might be stuck wondering what exactly you’re reacting to.
Environmental factors
Many different things in your environment like insect stings and pet dander can make you break out in hives. However, there can be a lot of other less obvious things in your world that can cause hives like exposure to sunlight, hot and cold temperatures, exercise, or tight clothing.
Most commonly, chronic hives are caused by an autoimmune process that self-resolves over months to years. Less frequently, systemic illnesses like lupus, lymphoma, thyroid disease or hepatitis may be the cause. Chronic hives could also be the result of ongoing stress.
How to manage chronic hives
While short-term, or acute, hives often go away on their own, chronic hives require diagnostic testing to discover your cause or eliminate suspicious triggers. Corticosteroids may help acutely but can cause side effects if used long term. Elevated doses of long-acting 2nd generation oral antihistamines (i.e. Cetirizine, Fexofenadine) can be effective in controlling hives in most patients. If these are ineffective, Xolair® – a biologic treatment that we offer at Apex Allergy and Asthma - can provide significant relief.
Some things that you can do on your own to manage your hives include using allergen-free soaps and detergents, avoiding hot baths and showers, and wearing loose-fitting clothes. If you suspect that a food is causing your hives, keep a food diary to help your allergist narrow down possible triggers.
To get to the root cause of your hives, schedule an appointment with our team today. Call or use our online booking tool and find relief!